P11.01 AMBULATORY ARTERIAL STIFFNESS INDEX (AASI) IS CORRELATED TO EA/EMAX, NOT PULSE WAVE VELOCITY IN PATIENTS WITH RESISTANT HYPERTENSION (RH) AND TYPE-II-DIABETES MELLITUS
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2010.10.114How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Objective: To examine if AASI is correlated to arterial stiffness in patients with RH and type-II-diabetes mellitus.
Methods: We included 87 patients. RH was defined according to guidelines from the American Heart Association.
Echocardiography was performed using GE Vivid 7and pulse wave analysis using Sphygmocor. All examinations were performed under standardized conditions. All analyses were done blinded offline using Echopac and customized software.
Ambulatory blood pressure (BP) measurement was done using Kivex TM 2430 and Spacelab 90217. All parameters were adjusted for sex, age, length of disease and heart rate using multiple linear regression. Spearman’s rank correlation was used to estimate correlation between groups.
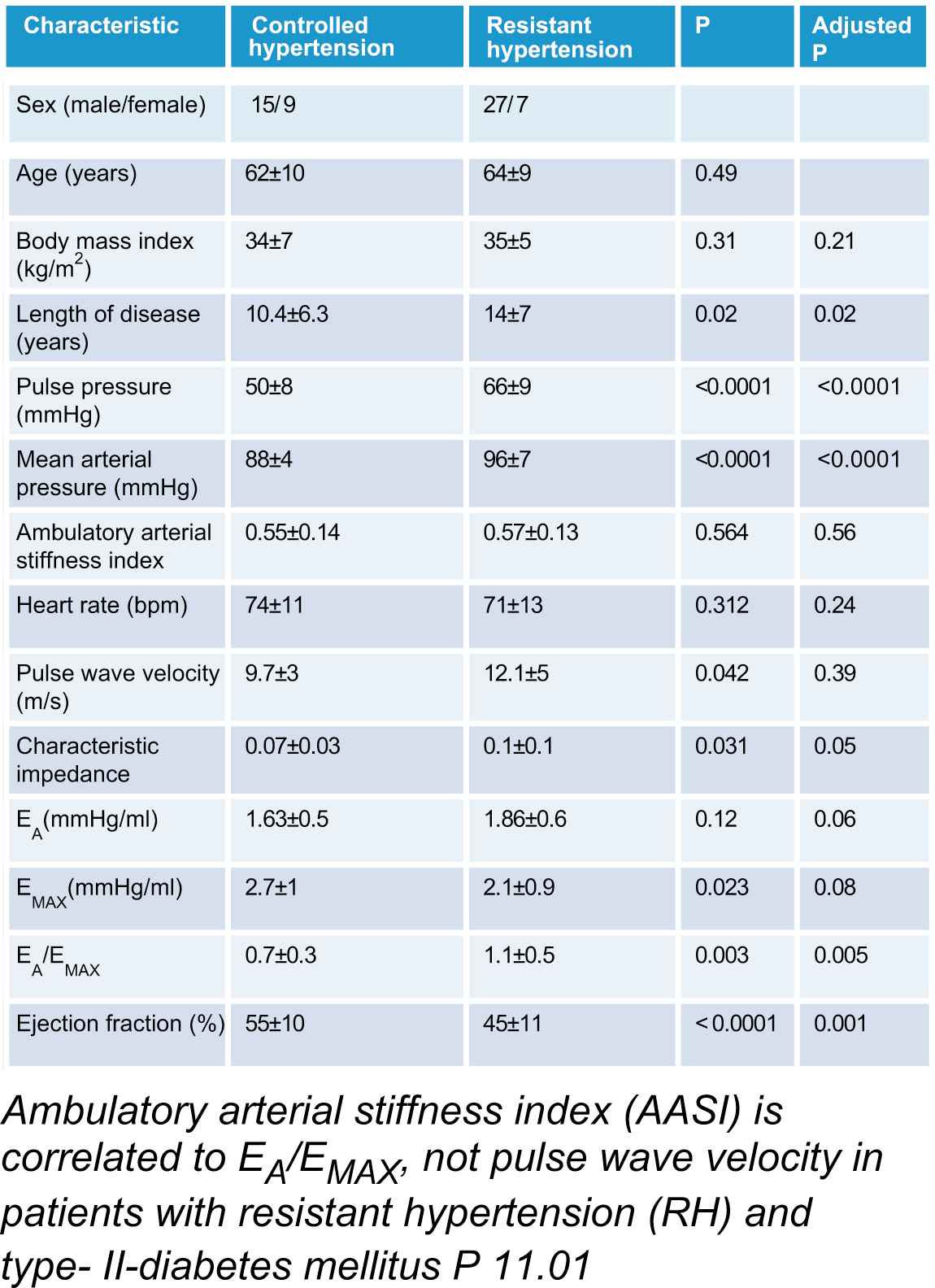
Results: 34 patients had RH and 24 had controlled hypertension (CH) leaving 29 with uncontrolled hypertension. See table 1 for patient characteristics. Patients were comparable with regards to age and body mass index. AASI did not differ significantly between groups. Pulse pressure, mean arterial pressure and length of disease varied significantly between groups. AASI and PWV was not correlated (Spearman’s rho = 0.08, P = 0.57).Neither was AASI and characteristic impedance (Spearman’s rho = 0.1, P=0.44) However when comparing AASI and EA/EMAX we found positive correlation (Spearman’s rho 0.36, P=0.006) and when comparing AASI and ejection fraction (Spearman’s rho = −0.29, P = 0.02) negative correlation.
Conclusion: AASI is not correlated to PWV or characteristic impedance, which are measures of arterial stiffness, but to EA/EMAX and ejection fraction, which might suggest that AASI does not reflect arterial stiffness, but ventriculo-vascular coupling.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - T.K. Sønder AU - B.B. Løgstrup AU - J. Lambrechtsen AU - L.M. Van Bortel AU - P. Segers AU - K. Egstrup PY - 2010 DA - 2010/12/02 TI - P11.01 AMBULATORY ARTERIAL STIFFNESS INDEX (AASI) IS CORRELATED TO EA/EMAX, NOT PULSE WAVE VELOCITY IN PATIENTS WITH RESISTANT HYPERTENSION (RH) AND TYPE-II-DIABETES MELLITUS JO - Artery Research SP - 178 EP - 178 VL - 4 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2010.10.114 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2010.10.114 ID - Sønder2010 ER -
