PO-17 A NEW ARTERIAL STIFFNESS INDEX PERMITTING ISOBARIC COMPARISONS
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2014.09.023How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Objectives: Arterial stiffness is pressure-dependent and comparisons among individuals and between groups should be made under isobaric conditions. Statistical methods are typically employed to adjust stiffness indices for pressure-dependence. In this ongoing study, we employ our new stiffness index, CPI, which allows for explicit evaluation at a reference pressure and stroke volume, to investigate its change with age and disease.
Methods: We studied twenty-three patients (n=23: 9 men and 14 women; mean age 70 years) that underwent diagnostic cardiac catheterization. Aortic pressure waveforms were used to evaluate CPI at a reference pressure of 80 mmHg and stroke volume of 100 mL. A closed-form expression of pressure-dependent compliance index, or CPI, was derived and computed for each subject. Linear regression was used to assess the trend of CPI with age.
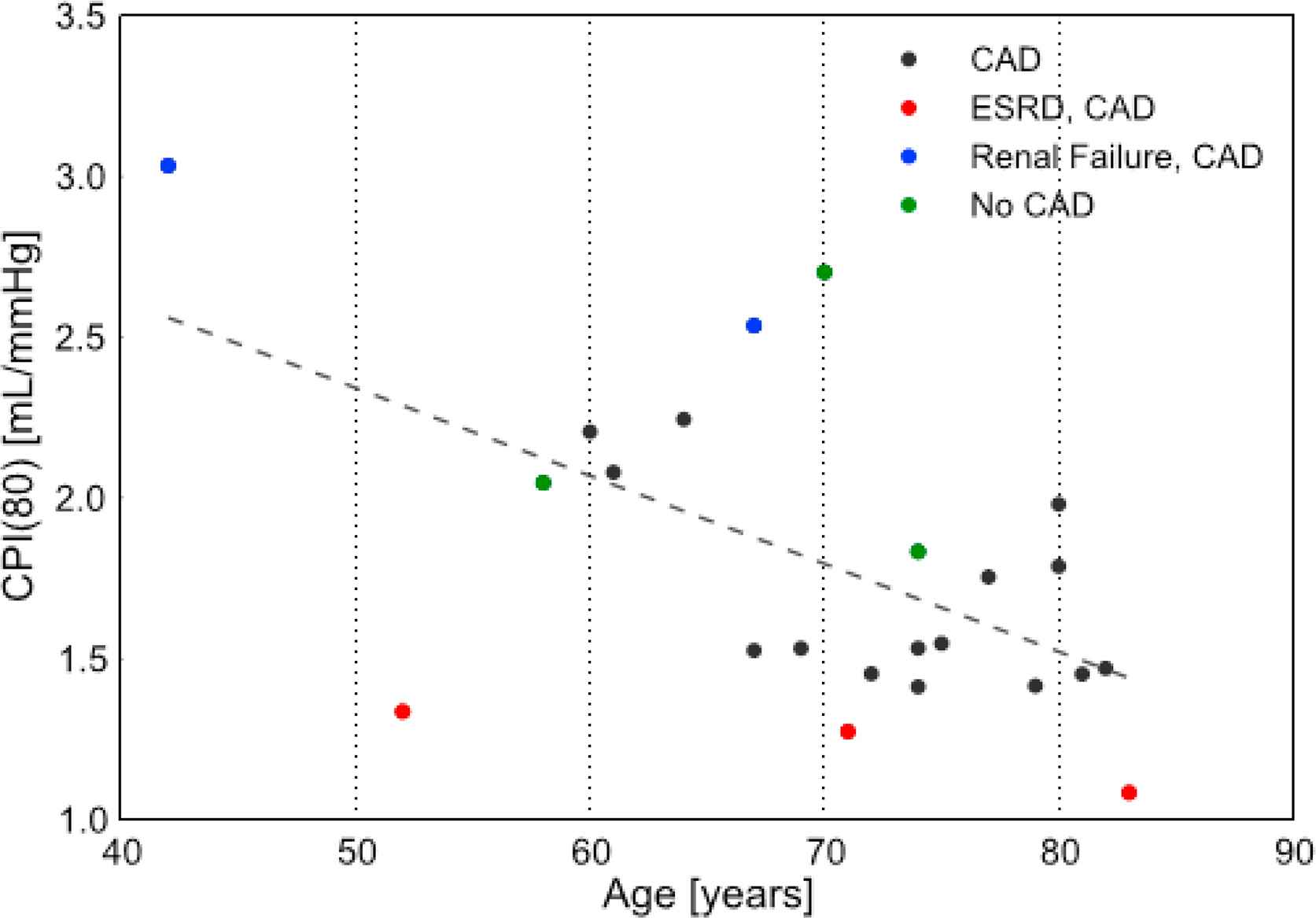
Results: CPI values ranged from 1.08 to 3.03 mL/mmHg. A negative correlation was found between CPI and age (r=−0.57, p<0.01). End-stage renal disease patients had the lowest values within their respective decade of age. Patients without coronary artery disease had the higher values within their decade.
Conclusions: CPI is an index of pressure-dependent arterial compliance. Its decrease with age, further exaggerated by presence of disease, is consistent with studies using other stiffness indices. The allowance for explicit evaluation at a common pressure relieves the need for statistical adjustments for pressure-dependence and permits a more individualized measure of arterial stiffness. Moreover, this allows separation of active and passive changes in arterial stiffness when cardiac properties or blood pressure levels are altered. Continuing studies will provide better sampling of age and disease states.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - T.S. Phan AU - K. Khaw AU - J.K.-J. Li PY - 2014 DA - 2014/11/04 TI - PO-17 A NEW ARTERIAL STIFFNESS INDEX PERMITTING ISOBARIC COMPARISONS JO - Artery Research SP - 172 EP - 173 VL - 8 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2014.09.023 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2014.09.023 ID - Phan2014 ER -
