P5.18 BRONCHOCONSTRICTION DOES NOT SIGNIFICANTLY ALTER CENTRAL HAEMODYNAMICS IN HEALTHY YOUNG ADULTS
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.073How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Background: Cardiovascular disease is the most frequent cause of death in people with chronic respiratory disease. Whether this association is due to shared comorbidities or adverse respiratory function exerting detrimental cardiovascular effects is unknown. This study aimed to determine the cardiovascular effect of methacholine-induced acute airway obstruction.
Methods: Fifteen healthy young adults (aged 22.9±2.5 years; 4 male; mean±SD) underwent a bronchial challenge test in which they were randomized in a blinded cross-over design to receive nebulized methacholine inhalation in serially increasing concentrations (from 0.39 to 25 mg/ml) or saline (0.9%; control) on two separate days. Airflow obstruction was assessed by forced expiratory volume at second (FEV1) and cardiovascular effects by brachial BP (oscillometry), central BP, augmentation index (AIx) and aortic stiffness (applanation tonometry).
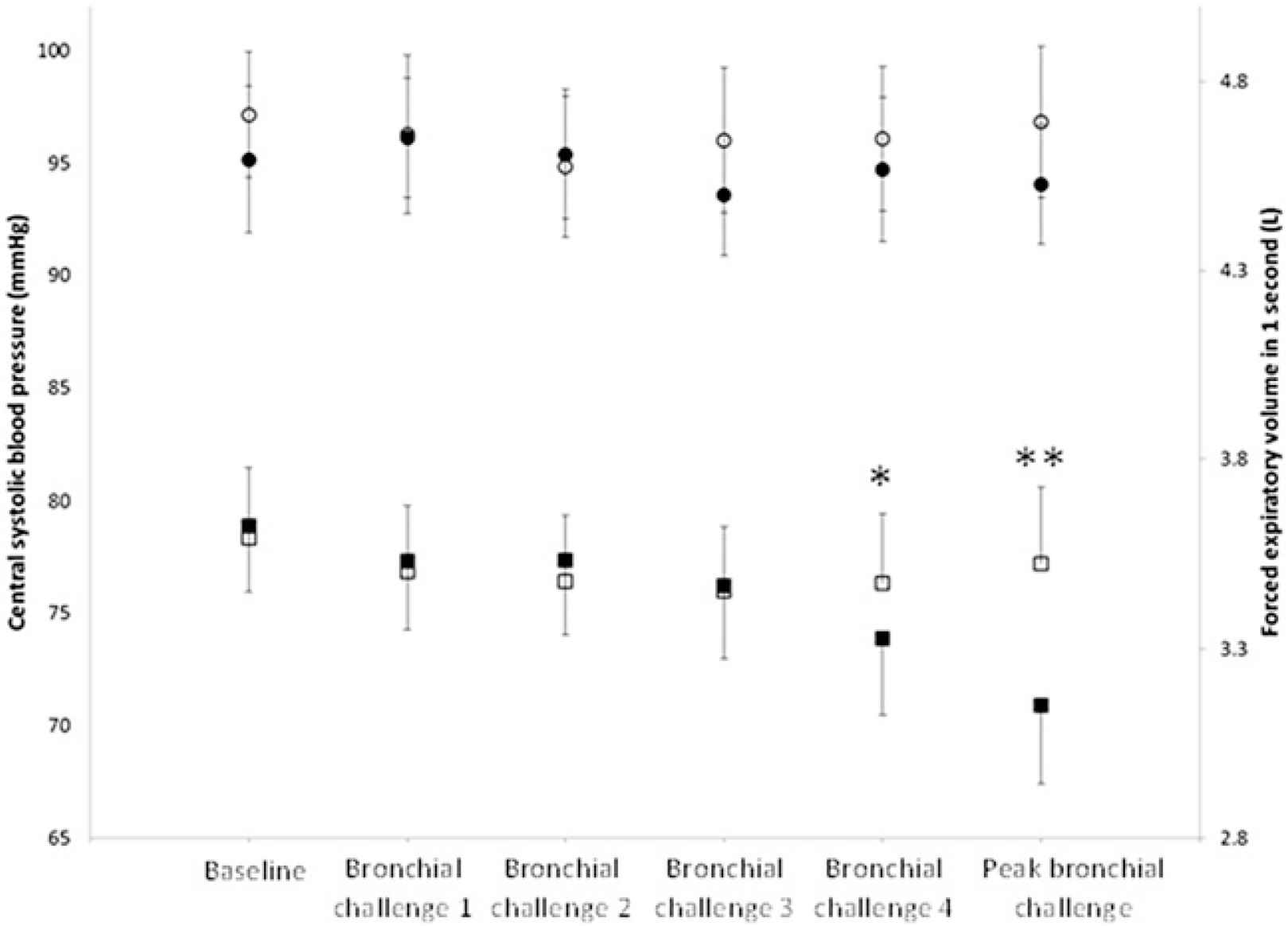
Results: Methacholine caused a significant decrease in FEV1 (bronchoconstriction) from baseline to peak inhalation compared with saline (−0.48±0.34 vs −0.07±0.16 L; p<0.001), but no significant between-group change in aortic stiffness (0.2±1.3 vs 0.8±1.8 m/s; p=0.20), AIx (1.6±7.0 vs 3.7±10.2%; p=0.49), brachial SBP (−3.3±7.6 vs −4.7±5.7 mmHg; p=0.59), central SBP (−1.1±5.2 vs −0.3±5.5 mmHg; p=0.73), or heart rate (0.4±7.1 vs −0.8±6.6 bpm; p=0.45). See figure for FEV1 and central SBP responses to inhaled methacholine (*P=0.012, **P<0.0001).
Conclusions: Methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction does not change cardiovascular function, as assessed by aortic stiffness, brachial and central BP in healthy young adults. A comparison of the responses in people with airway disease would be of interest and may help to elucidate the connection between cardiovascular and respiratory disease.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - J.E. Sharman AU - J. Marrone AU - J. Walls AU - D.P. Johns AU - R. Wood-Baker AU - E.H. Walters PY - 2011 DA - 2011/11/29 TI - P5.18 BRONCHOCONSTRICTION DOES NOT SIGNIFICANTLY ALTER CENTRAL HAEMODYNAMICS IN HEALTHY YOUNG ADULTS JO - Artery Research SP - 168 EP - 168 VL - 5 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.073 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.073 ID - Sharman2011 ER -
