P4.01 STRESS CALCULATIONS IN 3D RECONSTRUCTIONS OF ARTERIES: THE INFLUENCE OF AXIAL IMAGE RESOLUTION
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.046How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Computational modeling of the stress distribution in vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques facilitates identification of high stress locations which can be related to plaque rupture. The first step in doing 3D biomechanical stress simulations is to accurately re-create the artery geometry from histology or in-vivo imaging. This research investigated the influence of the axial sampling resolution of histology on the stress distribution in plaques.
A 3D reference geometry of a diseased human coronary artery was constructed based on 7 histological images with an axial spacing of 0.5 mm. Three under sampled models were generated: a 3D model based on four slices (1 mm spacing) and two 2D models based on one slice only (Figure 1). The stress distribution was calculated using the Finite Element Method (FEM).

3D geometries (lumen and lipid surfaces shown)
The under sampled 3D model underestimates the peak stress by approximately 3% (Figure 2). The peak stress in the 2D models is 6% higher in one case and 12% lower in the other case. It can be concluded that a lower axial sampling resolution leads to a lower stress estimation due to smoothing of the geometry. Performing 2D simulations results in a more unpredictable stress distribution in that slice. However, approximate stress values and the location of peak stresses can be predicted well with a 3D under sampled geometry, indicating that 1 mm axial sampling might be sufficient for clinical FEM studies.
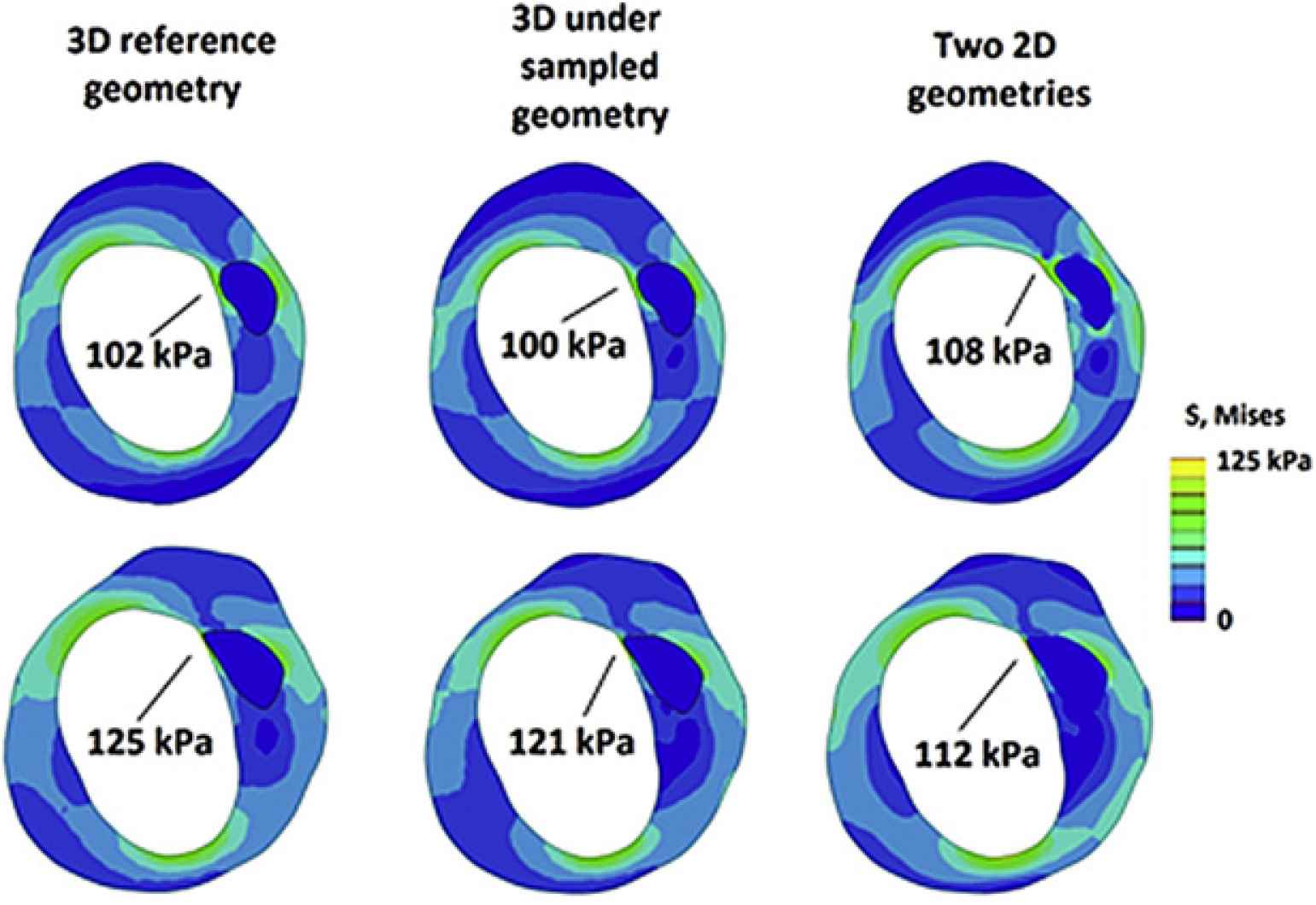
Von Mises stress distributions.
This research was supported by the Center for Translational Molecular Medicine and the Netherlands Heart Foundation (PARISk)
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - H.A. Nieuwstadt AU - A. Akyildiz AU - L. Speelman AU - J.J. Wentzel AU - R. Virmani AU - T. van der Steen AU - F. Gijsen PY - 2011 DA - 2011/11/29 TI - P4.01 STRESS CALCULATIONS IN 3D RECONSTRUCTIONS OF ARTERIES: THE INFLUENCE OF AXIAL IMAGE RESOLUTION JO - Artery Research SP - 159 EP - 159 VL - 5 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.046 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.046 ID - Nieuwstadt2011 ER -
